Executive Search
Five Sciences
Using one assessment could reveal the answer to one or two of these questions. But you would only see the partial picture.
Multiple sciences progressively reveal more of the entire person — what they do, how they do it and why they do the things they do. We also embrace a philosophy that measures both the presence and absence of behavior, and acceptance and avoidance. We use a data pool of millions of individuals collected over several decades to further refine our assessments.
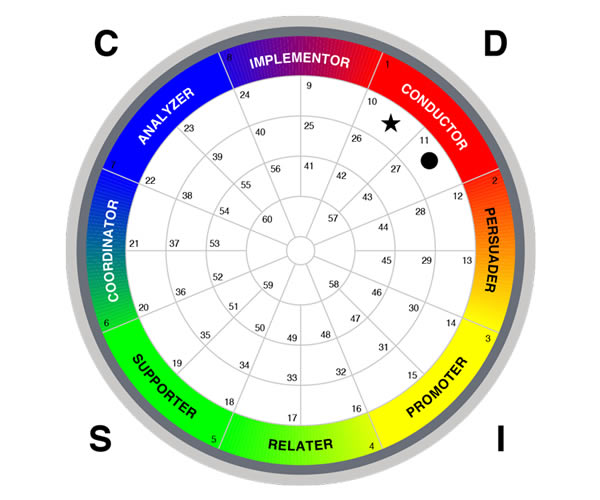
Behaviors (DISC)
Measured in four proportions (Dominance, Influence, Steadiness and Compliance), Behaviors/DISC reveal how an individual will perform, including how they prefer to communicate, what he or she will bring to a team, his or her ideal environment and possible limitations he or she may face.
Our behavioral research suggests that the most effective people are those who understand themselves, both their strengths and weaknesses, so they can develop strategies to meet the demands of their environment.
LeaderShift Assessments measuring Behaviors/DISC examine an individual’s dominance, influence, steadiness and compliance, revealing the ways in which one responds to the following:
- Problems and Challenges
- Influencing Others
- Pace of Environment
- Rules and Procedures
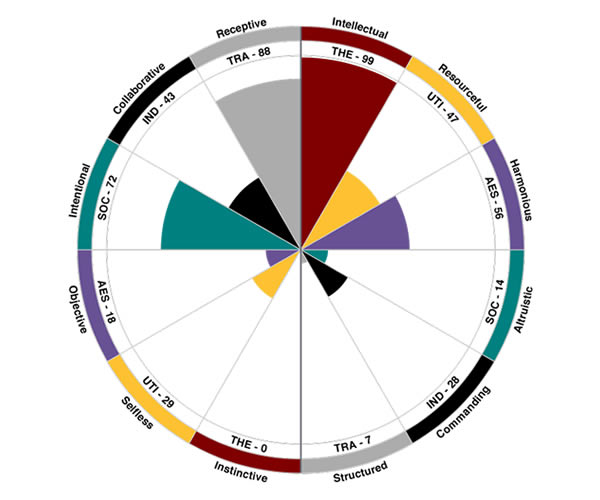
12 Driving Forces™ (Motivators/Values)
Driving forces uncovers what people value, motivates them and engages an individual in work and in life. At the core of 12 Driving Forces are 6 motivators, rooted in Eduard Spranger’s esteemed research from 1928. Backed by decades of research, LeaderShift Assessment reveals 12 Driving Forces that uniquely define what sparks movement and ambition in each of us.
Just as the LeaderShift Architect behavioral (or DISC) assessments help tell us how people behave and perform in a work environment, our 12 Driving Forces™ assessment reveals why they do what they do and what impacts their decision-making.
LeaderShift assessments measuring 12 Driving Forces examine the relative prominence of the following:
- Instinctive/Intellectual (Knowledge)
- Selfless/Resourceful (Utility)
- Objective/Harmonious (Surroundings)
- Intentional/Altruistic (Others)
- Collaborative/Commanding (Power)
- Receptive/Structured (Methodologies)
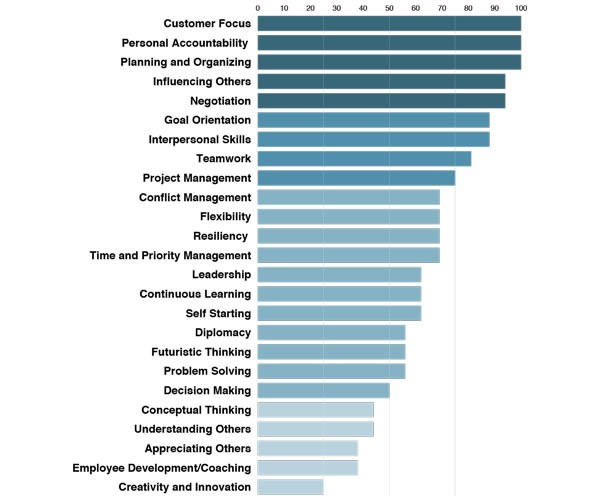
Competencies
Measuring 25 research-based personal skills directly related to the business environment. Applied in conjunction with a job benchmark, Competencies ensure the skills of each individual match the soft skills required by the job.
Research has validated that, for many jobs, personal/leadership skills (soft skills) are just as important as technical skills in producing superior performance. Personal/Leadership skills are often transferable to different jobs, whereas technical skills are usually more specific.
Our assessments measuring Competencies examine the level of development of 25 unique personal/leadership skills, ranking them from the most well developed skill to the one requiring the greatest level of further development.
While not every job requires the development of all 25 Competencies, the LeaderShift Assessment examines the following personal skills:
- Appreciating Others
- Conflict Management
- Continuous Learning
- Creativity and Innovation
- Conceptual Thinking
- Customer Focus
- Decision Making
- Diplomacy
- Employee Development/Coaching
- Flexibility
- Futuristic Thinking
- Goal Orientation
- Influencing Others
- Interpersonal Skills
- Leadership
- Negotiation
- Personal Accountability
- Planning and Organizing
- Problem Solving
- Project Management
- Resiliency
- Self Starting
- Teamwork
- Time and Priority Management
- Understanding Others
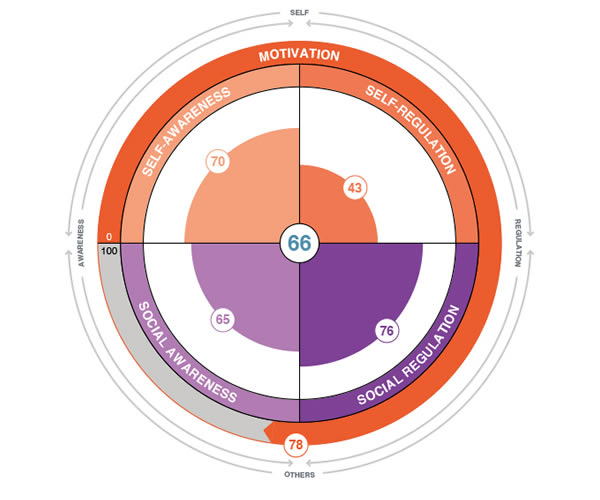
Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
Emotional Intelligence is an individual’s ability to sense, understand and effectively apply the power and acumen of emotions to facilitate high levels of collaboration and productivity.
Our research indicates that successful leaders and superior performers have well developed EQ skills. This enables them to work well with a wide variety of people and respond effectively to the rapidly changing conditions in the business world.
EQ examines five key areas pertaining to intrapersonal and interpersonal relations:
- Self Awareness
- Self Regulation
- Motivation
- Social Awareness
- Social Regulation
Acumen

Acumen (capacity/potential) is assessed using three dimensions of thought, analyzing both world and self-views:
- Intrinsic (feeling)
- Extrinsic (doing)
- Systemic (thinking)
Acumen, or a person’s keenness and depth of perception, the most important component of critical thinking and decision quality will identify how a person thinks. The LeaderShift Acumen indicators can be considered a lens that people use to filter information: do they process events from a people standpoint, a task standpoint or a system standpoint?
A person’s Acumen, or their clarity or understanding of a situation, could be directly related to their performance. Our assessments measuring Acumen examine the six dimensions:
- Understanding Others
- Practical Thinking
- Systems Judgment
- Sense of Self
- Role Awareness
- Self Direction



